The Headline “Is Recession coming to India?” is on fire these days.
And if you follow business news, I bet you must have gone through these headlines.
In the world of economics, “Recession” is a word that nobody would like to hear. And if there is even a minimum possibility of Recession to come in India, we must know about it and its consequences.
You must be wondering in the meantime that what actually the recession is and why it has got a bad name.
If so, there is nothing to worry about.
However, this article is not about the debatable topic “Is Recession coming to India?” . I would try to cover the same in some another post.
My main focus in this blogpost is to make you aware of the term “Recession”.
So we would be covering the basic definition of recession, its causes and indicators, and many more.
So if you too are excited like me, then definitely try to read this article till the end.
The Business Cycle
Before going to discuss about the Recession, you should know about the Business Cycle.
The business cycle, also known as the economic cycle refers to the changes in the growth of economic output while taking into account the constant rise in the economy’s “potential output.”
Here Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the measure of output, and Potential Output is the level of output that an economy can reach by using all of its resources, including labour, capital, raw materials, and technology.
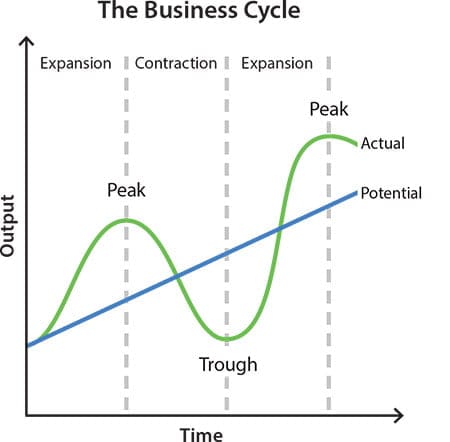
This graph shows the different phases of an Economy. There are four main phases in a business cycle. These are Expansion, Peak, Contraction, and Trough.
Expansion is the “normal” state of an economy. This is the period when the demand for goods and services is high, businesses grow their production and profits, employment or the job opportunities is high, and the stock market performs well.
Since people are buying and investing more, the prices begin to rise as the demands for goods and services starts increasing.
Peak is the highest point of the Expansion.
This is the time when the cost of the goods and services reaches the maximum limit. The economic output or the economic production is at its peak.
The Peak is usually seen as a turning point in the Contraction Phase.
Contraction is the period when there is a lower demand for the goods and services. This results in the low level of production in the economy. Businesses hire less workers and thus there is a high unemployment.
Since people tend to buy less, the cost of the goods and services begins to fall.
Eventually there comes a time when the economic production and the prices of the goods and services attain its lowest value.
This is known as the Trough.
Since the prices are at the lowest point, people start buying and investing again. Businesses start their production and the economy enters into a recovery phase.
The Trough is usually seen as a turning point into the expansion phase.
This is all how an economic cycle functions.
What is Recession?
There is no specific or standardized definition of Recession.
Economists define it using a number of indicators including high unemployment, negative GDP, decline in consumer spending among some of them.
“Recession” is the period when the economy stops growing and there is a massive slowdown in the economic activities followed by high unemployment.
The Recession is ‘technically’ defined as the period when the GDP of the Nation falls for two straight quarters i.e., When the GDP remains negative for two consecutive quarters or six months.
The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), which is a non-profit organization in the US, defines Recession as a period of significant economic downturn that can lasts for a few months to more than a year.
The NBER emphasizes that although a majority of recessions have in fact two consecutive quarters of negative real GDP growth, this is not always the case.
What are the Causes of Recession?
Recession in India and globally are mainly caused by the following factors-
1. Economic Shocks

These are the situations when there is a widespread damage to the economy. This consist of the natural disasters such as flood, earthquake, famine, pandemic, etc. and situations such as war or sudden terrorist attacks.
During economic shocks, people stop buying goods and hence there occurs a huge decline in the consumer demands. This results in the low-level of production and rise in unemployment, causing the economy to head towards recession.
2. Loss of Consumer Confidence
This situation arises when people/customers lose faith in the state of the economy. This is the time when people save as much money as they can and give up buying.
Gradually the demand for goods and services starts decreasing. As a result, businesses produce less and thus the GDP begins to decline.
3. High Interest Rates
Getting a loan is not affordable for most people when the interest rate is high.
This would compel consumers to cut back on their spending, especially on major purchases like a house or car.
4. Asset Bubbles
Asset Bubbles can be another cause for Recession.
But what is an asset bubble?
In asset bubble, the asset prices whether they are stock prices or real estate prices, undergo a rapid spike and move beyond their fundamentals. Eventually the demand begins to fall and the bubble bursts. As a result, investors lose money and their confidence collapses. They cut back on their spending which decreases the demand for goods and services in the economy. The economy slows down and finally goes into Recession.
The Recession of 2001 was primarily caused by the Dot Com Bubble burst of tech stocks in 2000, while the Great Recession occurred just after the crash of the housing market.
Indicators of Recession
There are many indicators that indicate the coming of a Recession. These include-
1. Fall in the Real GDP
2. Rise in unemployment
3. Stagnation of economic production
4. Decline in consumer spending
Slowdown vs. Recession vs. Depression
Although these words sound alike, they have different meanings.
Let’s see what distinguishes them.
Recession:
Recession refers to a phase of economic downturn for more than two quarters (six months).
It begins when the economic cycle hits its peak and ends as soon as it reaches its low i.e., the trough.
Depression:
Depression is the extended period of economic recession followed by a significant slowdown in the economic activity.
So we can say that when a recession turns out to be more severe and lasts for several years or even decades, it results into a depression.
The Great Depression of 1930s began in 1929 and lasted until around 1939.
Slowdown:
Slowdown simply refers that the GDP growth is still in the positive zone but the rate of increase has slowed.
Conclusion
This was all about the Guide to Recession in India.
I hope you got to learn a lot about recession from this article.
If you have any suggestion or doubt regarding this blog post, you can let me know in the comment section.
See you soon!!
Happy Investing✌️

